Kuvaterner Fayı Nedir
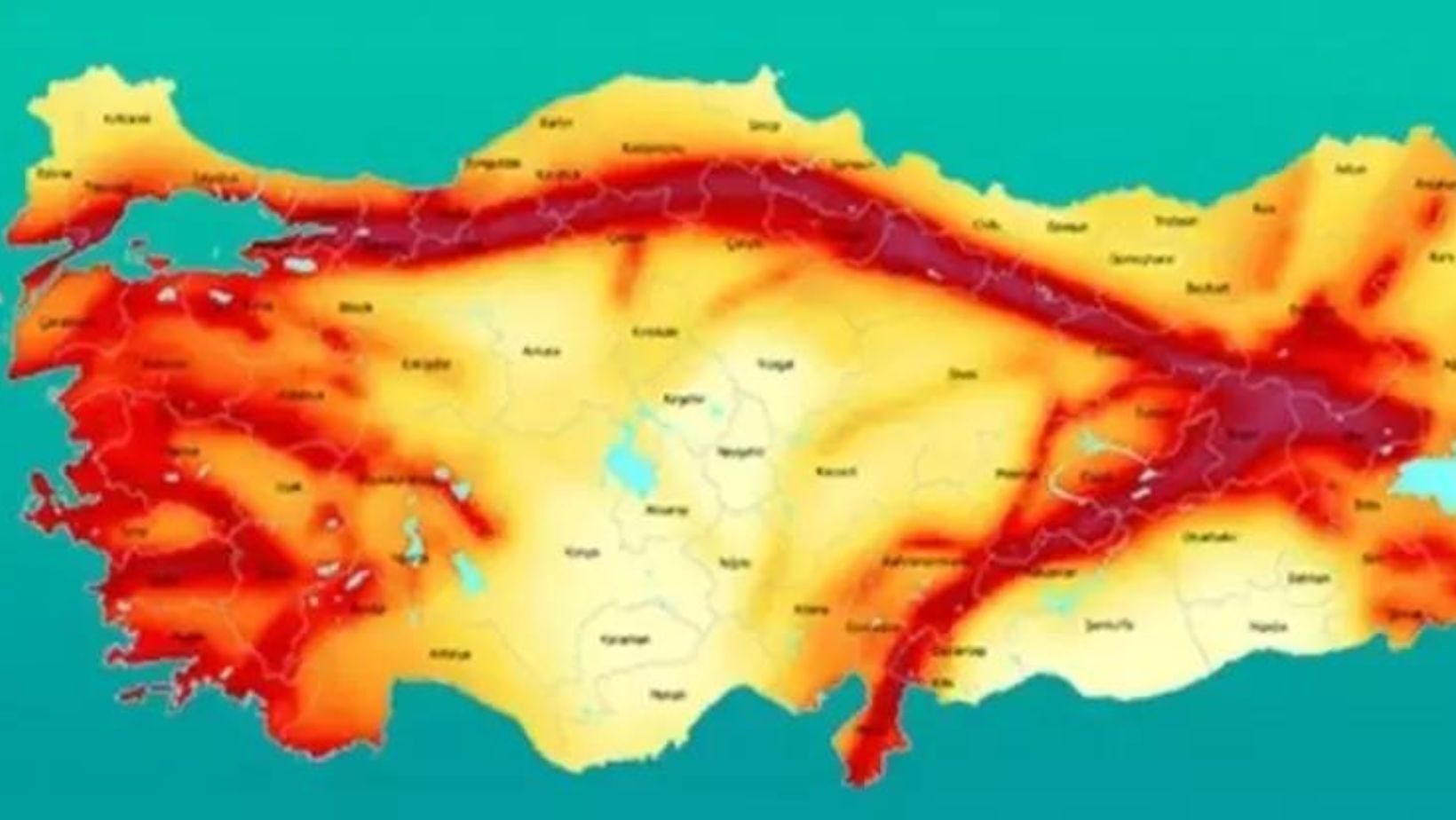
Quaternary faults occur due to tectonic forces that cause rocks to deform and slip along fault lines. They can be found in various regions around the world, including areas with active plate boundaries or regions undergoing uplift or subsidence. Understanding these faults is crucial for assessing earthquake hazards and developing effective mitigation strategies.
By studying Kuvaterner Fayı Nedir quaternary faults, geologists can gather valuable information about past earthquakes and determine their recurrence intervals. This knowledge helps us better understand the potential for future seismic events and allows us to make informed decisions regarding land use planning and infrastructure development in vulnerable areas.
Definition of Quaternary Fault
A quaternary fault refers to a type of geological fault that has been active during the Kuvaterner Fayı Nedir Quaternary period, which encompasses the last 2.6 million years. These faults are characterized by their relatively recent activity, making them of great interest to geologists and seismologists studying earthquake hazards.
Quaternary faults can be found in various tectonic settings, including areas where tectonic plates converge, diverge, or slide past each other. They are typically associated with regions of high seismic activity and have the potential to generate significant earthquakes.
The movement along these faults occurs as a result of stress accumulation in the Earth’s crust over time. When this stress exceeds the strength of the rocks, it is released through sudden movements known as earthquakes. The displacement caused by these fault movements can range from a few millimeters to several meters.
Characteristics of Quaternary Faults
Quaternary faults, also known as Kuvaterner Fayı in Turkish, exhibit distinct characteristics that set them apart from other types of faults. Understanding these characteristics is crucial for geologists and seismologists in assessing the potential risks associated with these faults. So, let’s delve into the key features of quaternary faults:
- Recent Activity: Quaternary faults are characterized by their relatively recent activity within the past 1.6 million years. Unlike older faults that may have ceased movement long ago, quaternary faults still possess
the capacity to generate earthquakes and shape the landscape around them.
- Displacement: One notable characteristic of quaternary faults is their ability to cause significant displacement along fault lines during seismic events. The amount of displacement can vary widely depending on factors such as fault type and tectonic forces involved. This movement can result in visible offsets in rock layers or even changes in landforms.
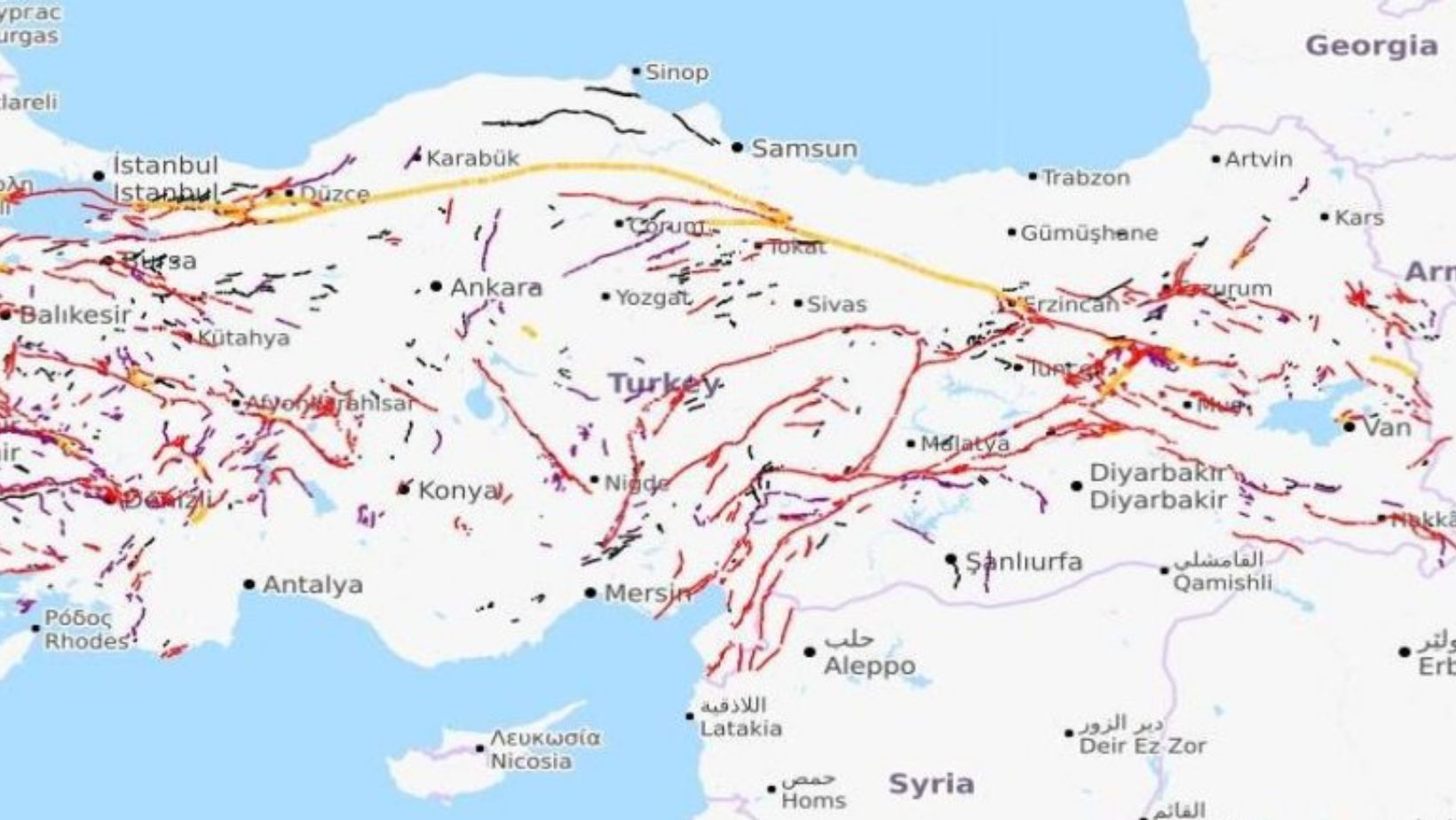
- Segmentation: Quaternary faults often exhibit a segmented nature, meaning they consist of multiple interconnected fault segments rather than one continuous line. These segments can have different orientations and slip rates, further complicating fault behavior analysis.
- Surface Ruptures: When a significant earthquake occurs along a quaternary fault, it may cause surface rupture – where the ground breaks and displaces along the fault trace at or near the Earth’s surface. These ruptures can be several kilometers long and provide valuable evidence about past seismic events.
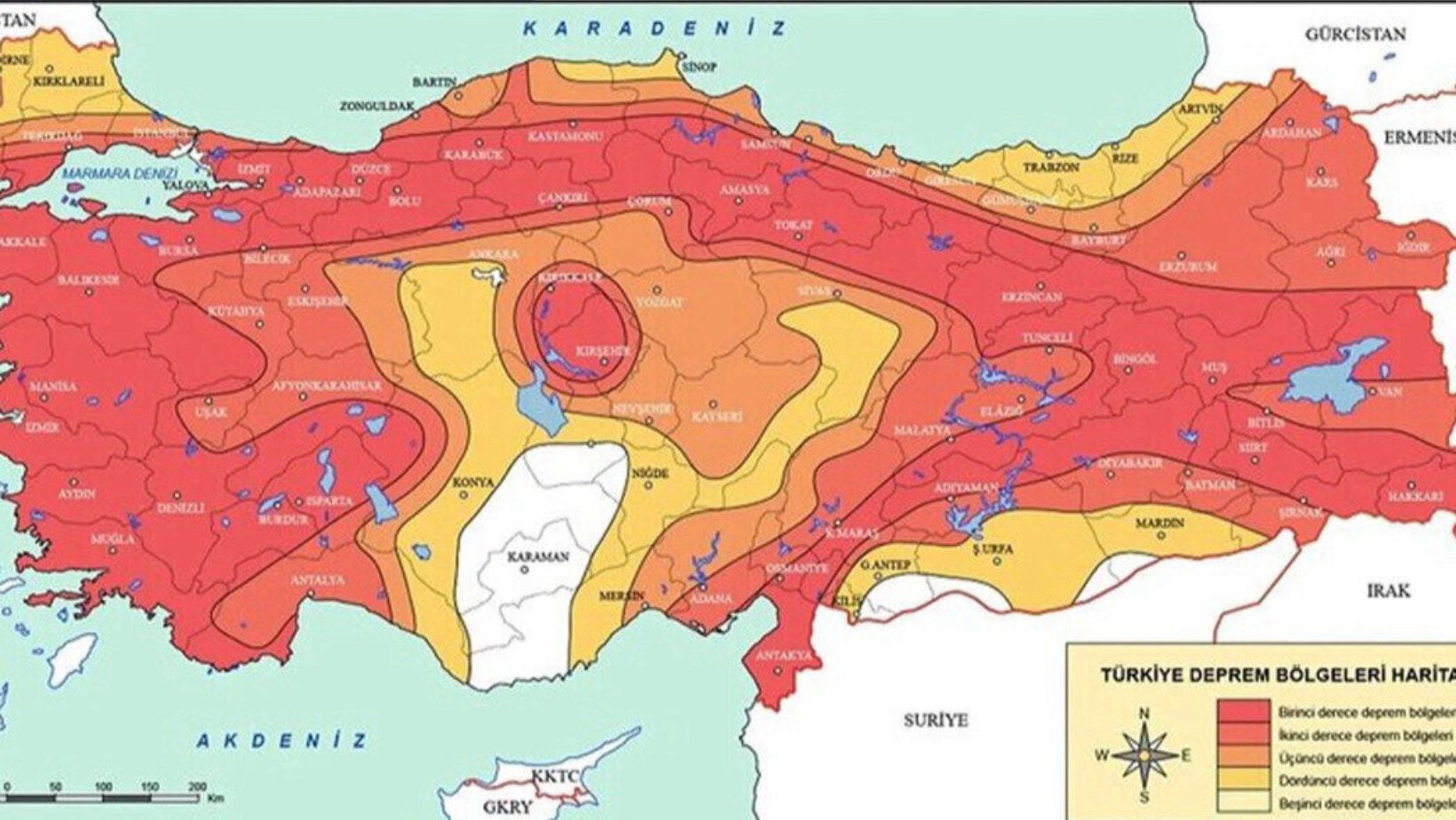
- Seismic Hazard Potential: Due to their relatively recent activity, quaternary faults pose a higher seismic hazard potential compared to older inactive faults. Understanding their characteristics helps scientists estimate earthquake recurrence intervals and predict future seismic events more accurately.


 the capacity to generate earthquakes and shape the landscape around them.
the capacity to generate earthquakes and shape the landscape around them.






















































































