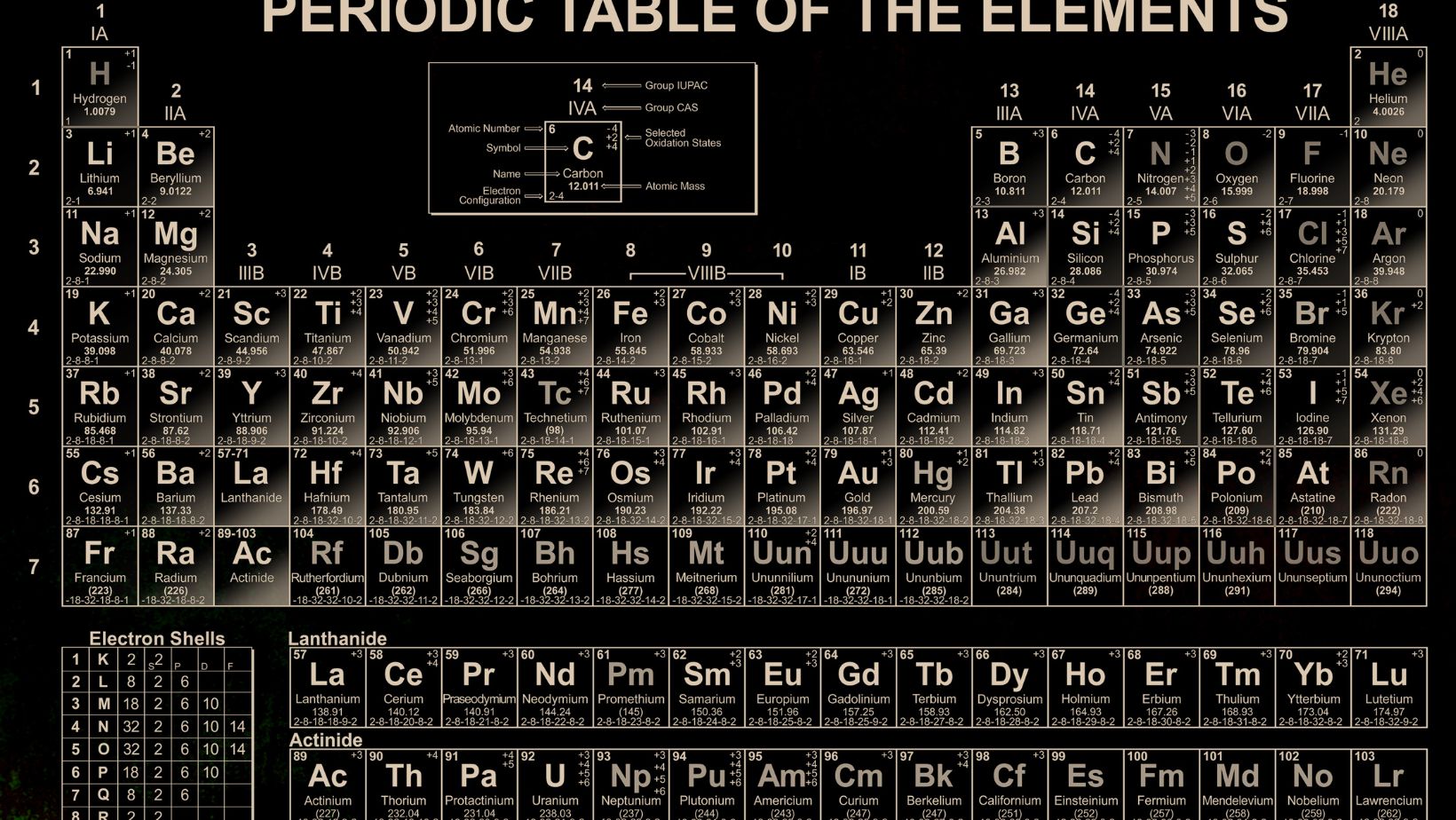
Bảng Nguyên tố Hóa Học
Hey there! Are you curious about the fascinating world of chemistry? Well, you’re in luck because today, I’ll be introducing you to a key tool that every chemistry enthusiast needs to know about – the “bảng nguyên tố hóa học” or the periodic table of elements.
The periodic table is like a map that guides us through the vast landscape of chemical elements. It’s a visual representation of all the building blocks that make up our universe – from the tiniest atoms to the largest molecules. With its rows and columns, the periodic table organizes elements based on their properties, such as atomic number, atomic mass, and electron configuration.
What is The Periodic Table of Elements?
Definition And Purpose
The Periodic Table of Elements, also known as “bảng nguyên tố hóa học” in Vietnamese, is a vital tool in the field of chemistry. It serves as a visual representation and organizational structure for the building blocks of the universe – the chemical elements.
The main purpose of the periodic table is to organize the elements based on their properties, enabling chemists to understand and predict their behavior. It provides a systematic way to categorize the elements and serves as a reference guide for various properties such as atomic number, atomic mass, electronic configuration, and chemical reactivity.
Key Components of The Periodic Table
Atomic Number
The atomic number in the bảng nguyên tố hóa học is a key component of the Periodic Table. It represents the number of protons in an atom’s nucleus, which determines its unique identity as an element. The atomic number is crucial for organizing the elements in the Periodic Table because it determines their position and order.
Element Symbol
Every element in the Periodic Table is assigned a unique element symbol, another important component of the bảng nguyên tố hóa học. These symbols are usually one or two letters derived from the element’s name, often in English or Latin. They provide a shorthand way to represent elements in chemical equations and formulas, making it easier for scientists to communicate and work with these elements.
Atomic Weight
The atomic weight, also known as atomic mass, is a significant characteristic of elements in the Periodic Table. It represents the average mass of the atoms of an element, taking into account the different isotopes and their abundance. The atomic weight is crucial for understanding the relative sizes of atoms and their positions in the Periodic Table. It helps determine trends in properties and behaviors of elements as well.
Organization of The Periodic Table
Groups And Periods
One of the key aspects of the Periodic Table is its organization into groups and periods. The groups are the vertical columns, while the periods are the horizontal rows. Each group contains elements with similar properties, while each period represents the energy level or shell of the elements.
- The groups are numbered from 1 to 18, and they are also given names based on their properties. For example, Group 1 elements are known as alkali metals, and Group 17 elements are called halogens.
- The periods are numbered from 1 to 7, and they indicate the number of electron shells an element’s atoms have. For instance, elements in Period 1 have only one electron shell, while elements in Period 2 have two electron shells.
Representative Groups
The representative groups, also known as the main group elements, are the elements found in Groups 1, 2, and 13 to 18 of the Periodic Table. These elements exhibit a wide range of chemical properties and play a crucial role in various industrial and biological processes.
- The alkali metals in Group 1 are highly reactive and are known for their low melting points and the ability to easily lose electrons.
- The alkaline earth metals in Group 2 have similar characteristics to alkali metals, but they are slightly less reactive and have higher melting points.
- The elements in Group 17, the halogens, are highly reactive nonmetals and are known for their tendency to gain electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration.
- The noble gases in Group 18 are characterized by their extremely low reactivity and stable electron configurations, making them chemically inert.
Transition Metals And Inner Transition Metals
The transition metals, found in the d-block of the Periodic Table, are known for their variable valence states, colorful compounds, and ability to form complex ions. They exhibit a wide range of physical and chemical properties and are often used as catalysts in chemical reactions.
On the other hand, the inner transition metals, located in the f-block, are known for their unique electronic structures and radioactive properties. The lanthanides are the elements from cerium (Ce) to lutetium (Lu), while the actinides are the elements from thorium (Th) to lawrencium (Lr). These elements have a variety of applications, including in nuclear power generation and medical imaging.
Importance of The Periodic Table
The Periodic Table of Elements is a powerful tool in the field of chemistry. It allows scientists to predict element properties, facilitate chemical reactions, and drive scientific research and discovery. By leveraging the knowledge contained within the table, we are able to unlock the mysteries of the elements and push the boundaries of chemical understanding. The Periodic Table of Elements is a fundamental tool in the field of chemistry. Its applications and importance cannot be overstated. By harnessing its power, scientists continue to make groundbreaking discoveries and advance our understanding of the world around us.