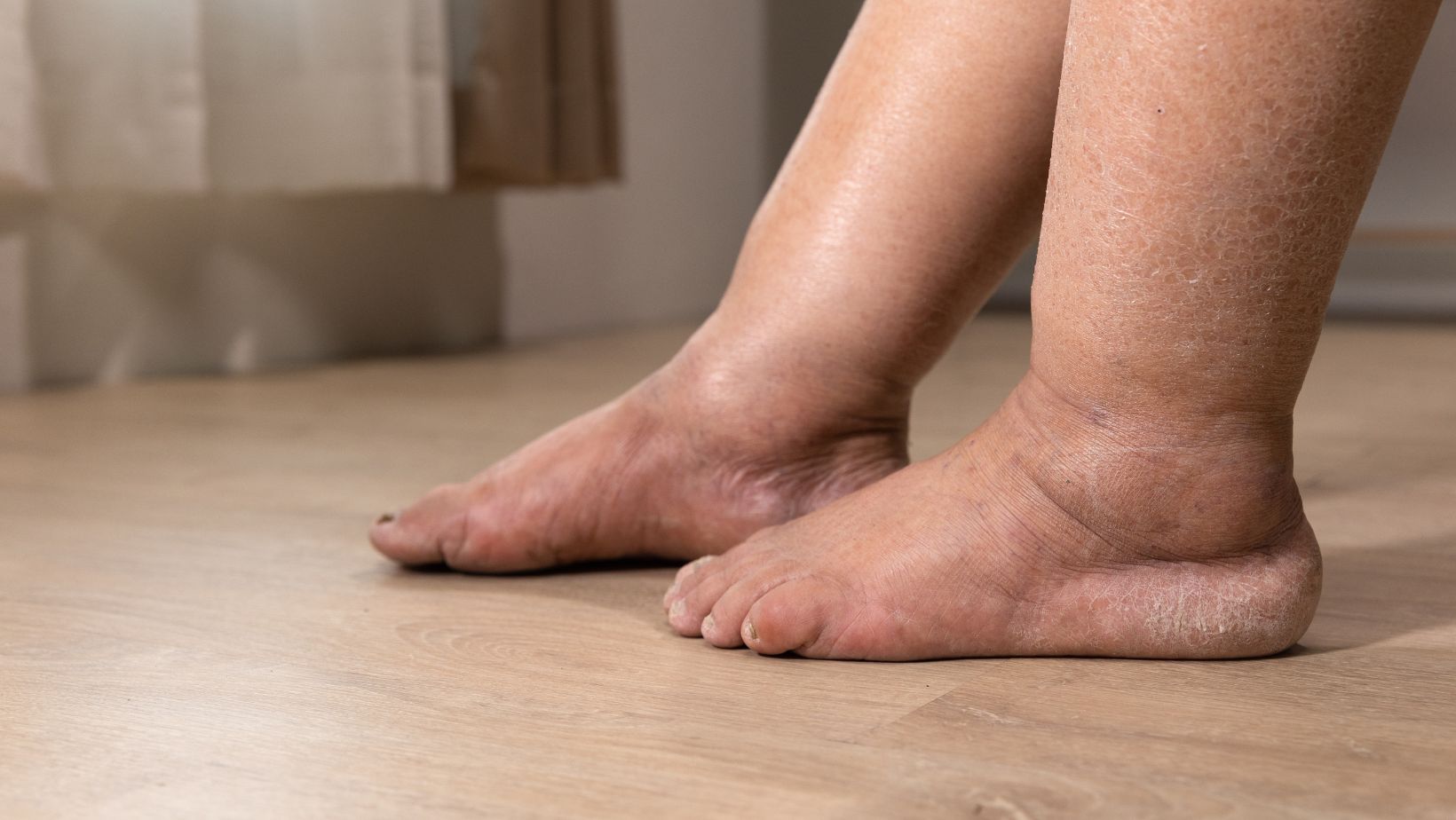
Edema, a condition characterized by the accumulation of fluid in the body’s tissues, can manifest in various parts of the body. However, it is often most noticeable in the hands and abdomen. As someone who has encountered this issue firsthand, I understand the discomfort and frustration it can cause. In this article, I’ll delve into the causes of edema, explore why it tends to be more pronounced in the hands and abdomen, and provide some practical tips for managing and reducing its symptoms. Whether you’re dealing with edema yourself or simply curious about this common condition, read on to gain a better understanding of how it affects the body and what you can do about it.
Edema Can Best Be Observed In
Edema is a common condition characterized by the accumulation of fluid in the body’s tissues. It can occur in various parts of the body, but it is often most noticeable in the hands and abdomen. As someone who has experienced edema firsthand, I can attest to the discomfort and frustration it can cause.
To understand edema, it’s important to know that our bodies rely on a delicate balance of fluid. This balance is maintained by our blood vessels and lymphatic system. However, when something disrupts this balance, such as an injury, certain medical conditions, or even pregnancy, excess fluid can accumulate in tissues and cause swelling.
The accumulation of fluid may be caused by several factors, including:
- Increased capillary pressure: When the pressure in the blood vessels increases, it can cause the fluid to leak out into the surrounding tissues.
- Decreased oncotic pressure: The oncotic pressure is the pressure exerted by proteins in the blood vessels. When this pressure decreases, it can lead to fluid retention.
- Lymphatic system dysfunction: The lymphatic system plays a crucial role in draining excess fluid from the tissues. If the lymphatic system is not functioning properly, fluid accumulates, leading to edema.
Edema can be a symptom of an underlying health condition, such as heart failure, kidney disease, or liver cirrhosis. It can also be a side effect of certain medications or prolonged sitting or standing.
Causes of Edema
Fluid Retention
One of the primary causes of edema is fluid retention in the body’s tissues. When the balance between the amount of fluid being pushed out by the capillaries and the amount being drawn back in by the veins is disrupted, excess fluid accumulates in the tissues, leading to swelling. This can be caused by various factors, such as:
- Increased capillary pressure: When the pressure inside the tiny blood vessels called capillaries increases, it can push fluid out into the surrounding tissues, resulting in edema.
- Decreased oncotic pressure: Oncotic pressure is the force that helps draw fluid back into the capillaries from the tissues. If the oncotic pressure decreases, such as in conditions like liver disease or malnutrition, fluid may not be effectively pulled back in, leading to edema.
- Lymphatic system dysfunction: The lymphatic system plays a crucial role in removing excess fluid and waste from the body. When the lymphatic system fails to function properly, fluid can accumulate in the tissues, causing edema.
Inflammation
Inflammatory processes within the body can also contribute to the development of edema. Inflammation is the body’s response to injury or infection, and it often involves an increase in blood flow to the affected area. This increased blood flow can result in localized swelling and edema as the capillaries become more permeable and allow fluid to escape into the surrounding tissues.
Medications
Certain medications can cause edema as a side effect. This is because some medications may interfere with the body’s ability to regulate fluid balance or increase blood flow to certain areas. Common culprits include:
- Calcium channel blockers: These medications, commonly used to treat high blood pressure or heart conditions, can cause peripheral edema by relaxing blood vessels and allowing fluid to leak out into the tissues.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): Some NSAIDs, like ibuprofen and naproxen, have been known to contribute to edema, especially with long-term use.
- Corticosteroids: These anti-inflammatory medications can cause edema by increasing sodium and fluid retention in the body.
Remember, these are just a few examples of medications that can cause edema. It’s always important to consult with a healthcare professional if you are experiencing edema, especially if it is accompanied by other concerning symptoms.
Now that we understand some of the common causes of edema, let’s explore why it is more pronounced in the hands and abdomen and discuss practical tips for managing and reducing its symptoms.

























































































